Topics: Finance and Accounting Outsourcing Services, Order-to-cash cycle
The 8 Stages of the Essential Order-to-Cash Process Explained
Posted on May 23, 2024
Written By Priyanka Rout

Introduction
Gaining new customers is a significant achievement that demands coordinated efforts across various teams. But the real challenge begins after closing the deal or receiving that first order. This is where the order-to-cash outsourcing process comes into play, an essential yet often complex part of the end-to-end business lifecycle.
The findings of a 2020 BCG report on O2C platforms suggest that businesses implementing these platforms and restructuring their processes can increase annual revenues by 1% to 3%.
From artisanal jam makers to t-shirt creators and bulk vendors of roofing tiles, every business that sells goods engages in the O2C process. While some business owners are more familiar with it than others, those who deeply understand and address the intricacies of this process often achieve greater efficiency and enjoy the benefits of satisfied customers, staff, and vendors.
By producing high-quality products and services that foster customer satisfaction, companies can successfully boost their revenue. Implementing robust order fulfillment practices can enhance customer experiences and drive profitability. Understanding the order to cash service process is key to establishing effective order fulfillment and improving financial performance. In this article, we will dive into the importance of the O2C process, its significance, and the common phases that constitute an effective O2C process.
What is the O2C Process and Why is it Important?
The Order-to-Cash (O2C) process covers everything from collecting payments and shipping products to creating invoices and keeping records. Despite its importance, the O2C process is often overlooked.
However, O2C is crucial as it impacts revenue, customer retention, engagement, and overall company growth through efficient practices, such as:
- Accelerating order fulfillment to meet customer demands swiftly.
- Streamlining the purchasing journey for customers, making it easier and more intuitive.
- Proactively avoiding backorders to maintain seamless operations.
- Guaranteeing precise order processing to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Demonstrating brand trustworthiness and expertise through consistent reliability.
- Minimizing the necessity for customer assistance with smoother processes.
- Enhancing record precision and data reporting for better decision-making.
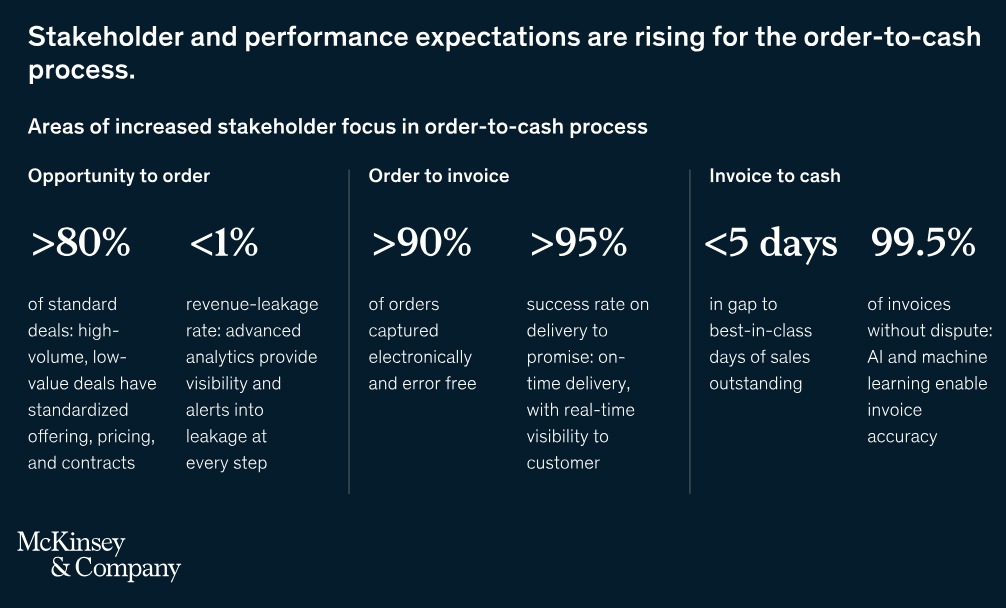 A snapshot of how stakeholder and performance expectations are rising for the order to cash process; Source: McKinsey & Company
A snapshot of how stakeholder and performance expectations are rising for the order to cash process; Source: McKinsey & Company
Business Functions in Order-to-Cash Cycle
In the order-to-cash outsourcing cycle, different parts of the business handle specific tasks:
- Taking Orders (Order Management): Making sure products are ready and delivered on schedule.
- Sales: Talking about prices and payment plans with customers.
- Getting Paid (Accounts Receivable): Collecting payments and sorting out any problems with orders.
- Keeping Track (Accounting): Keeping records of the money coming into the company.
- Managing Stock (Inventory Management): Checking how much stuff we have and letting the order team know.
- Looking at Data (Reporting and Data Management): Watching trends and suggesting ways to make the whole process better.
 Percentage of companies that use selected O2C leading practices; Source: Salesforce
Percentage of companies that use selected O2C leading practices; Source: Salesforce
The Tangible Benefits of Order-to-Cash Transformation
When done correctly, transforming the order-to-cash process can have a significant impact. Recent research conducted by BCG indicates companies can experience the following advantages:
- Cost Savings: Costs can be reduced by 15% to 30% through automated order creation, digital invoicing, fewer disputes, and reduced penalties for late or incomplete orders.
- Faster Payments: Days sales outstanding can be reduced by up to 30%, thanks to better stock management, quicker processes, and proactive collection efforts.
- Customer Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction can improve significantly due to a smoother order process, real-time complaint resolution, fewer invoice disputes, and greater transparency.
- Employee Satisfaction: Employee satisfaction can increase as repetitive tasks are minimized, allowing more time for strategic work and fostering innovation.
Order-to-cash transformation not only makes resource use more efficient, improves cash flow, and enhances transparency, but it also transforms an administrative function into a business driver. By integrating end-to-end process data, companies gain new insights that can improve service.
Click here to learn how O2C outsourcing can help you master the O2C process.
The 8 Stages of Order-to-Cash Outsourcing Process Explained
Stage 1: Order Management
Definition and Significance of Order Management
Order management refers to the process of receiving, tracking, and fulfilling customer orders. It is a critical component of the Order to Cash (O2C) cycle as it ensures that orders are processed accurately and efficiently, directly impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Steps Involved in Order Entry and Verification
- Order Entry: Capturing the order details from customers through various channels like online portals, phone calls, or emails.
- Order Verification: Ensuring the accuracy of the order details, checking product availability, and verifying customer information.
- Order Confirmation: Sending an acknowledgment to the customer, confirming that the order has been received and is being processed.
- Order Validation: Cross-checking order details with internal systems to ensure everything is correct before proceeding.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Order Management
- Data Entry Errors: Implement automated order entry systems to minimize manual input and errors.
- Order Duplication: Use order management software that tracks all orders in real-time to prevent duplicates.
- Inventory Mismatches: Integrate inventory management systems to provide accurate stock levels and prevent over-promising.
- Order Delays: Streamline order processing workflows and enhance communication between departments to reduce delays.
Stage 2: Credit Management
Role of Credit Management in the O2C Process
Credit management involves assessing the creditworthiness of customers, setting credit terms, and managing the associated risks. It ensures that sales are made to customers who are likely to pay on time, thereby protecting the company’s cash flow and minimizing bad debts.
Assessing Customer Creditworthiness
- Credit Reports: Review credit reports from agencies to evaluate the financial health of customers.
- Financial Statements: Analyze customers’ financial statements to assess their ability to pay.
- Payment History: Check the customer’s payment history with your company and other vendors.
Setting Credit Limits and Terms
- Credit Limits: Establish credit limits based on the customer’s creditworthiness and order history.
- Payment Terms: Define payment terms that balance the need for prompt payment with customer relationships, such as Net 30 or Net 60 days (about 2 months).
Strategies for Effective Credit Risk Management
- Regular Credit Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of customer credit limits and terms to adapt to changing financial conditions.
- Credit Insurance: Consider credit insurance to protect against potential defaults.
- Credit Hold Policies: Implement credit hold policies for customers who exceed their credit limits or have overdue payments.
Stage 3: Order Fulfillment
Overview of Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment encompasses the complete process of receiving, processing, and delivering orders to customers. It involves coordination between multiple departments to ensure orders are delivered accurately and on time.
Coordination Between Inventory, Warehousing, and Logistics
- Inventory Management: Maintain accurate inventory records to ensure stock availability.
- Warehousing: Efficiently pick, pack, and prepare products for shipment.
- Logistics: Plan and execute the transportation of goods to the customer.
Ensuring Timely and Accurate Delivery
- Real-Time Tracking: Use tracking systems to monitor the status of orders.
- Delivery Schedules: Optimize delivery routes and schedules to meet customer expectations.
- Quality Control: Implement checks to ensure the correct items are delivered in good condition.
Best Practices for Optimizing Order Fulfillment
- Automate Processes: Use automation tools to streamline order processing and reduce manual errors.
- Warehouse Layout: Design warehouse layouts to facilitate efficient picking and packing.
- Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers to ensure consistent stock levels.
Stage 4: Shipping and Logistics
Importance of Efficient Shipping and Logistics
Efficient shipping and logistics are crucial for meeting customer expectations, reducing costs, and enhancing overall customer satisfaction. It involves selecting appropriate shipping methods and carriers and managing the entire logistics chain.
Selecting the Right Shipping Methods and Carriers
- Carrier Evaluation: Assess carriers based on cost, reliability, and service levels.
- Shipping Methods: Choose shipping methods (e.g., ground, air, sea) based on delivery speed and cost considerations.
Tracking Shipments and Handling Returns
- Shipment Tracking: Provide customers with tracking information to monitor their orders.
- Returns Management: Implement a clear and efficient process for handling returns and exchanges to maintain customer satisfaction.
Impact of Shipping on Customer Satisfaction
- On-Time Delivery: Ensure timely delivery to meet customer expectations.
- Delivery Options: Offer multiple delivery options to cater to different customer needs.
- Communication: Keep customers informed throughout the shipping process to build trust and transparency.
Stage 5: Invoicing
Process of Generating Accurate Invoices
Invoicing involves creating detailed bills for the products or services provided to customers. Accuracy in invoicing is crucial to ensure timely payments and maintain good customer relationships.
Key Components of an Invoice
- Invoice Number: Unique identifier for tracking.
- Customer Details: Name, address, and contact information.
- Itemized List: Description of goods/services provided, quantities, and prices.
- Total Amount Due: Sum of all items, including taxes and discounts.
- Payment Terms: Due date and payment instructions.
Common Invoicing Errors and How to Avoid Them
- Incorrect Details: Double-check customer and order details before sending invoices.
- Missing Information: Ensure all necessary information is included.
- Calculation Errors: Use automated invoicing systems to avoid manual calculation mistakes.
Automation Tools for Streamlining Invoicing
- Invoicing Software: Utilize software to generate and send invoices automatically.
- Integrated Systems: Link invoicing systems with order and inventory management to ensure data consistency.
Stage 6: Accounts Receivable
Managing Accounts Receivable Effectively
Accounts receivable management involves tracking and collecting payments from customers. Effective management ensures steady cash flow and minimizes overdue accounts.
Techniques for Timely Collection of Payments
- Prompt Invoicing: Send invoices immediately after order fulfillment.
- Payment Reminders: Use automated reminders for upcoming and overdue payments.
- Incentives for Early Payment: Offer discounts for early payments to encourage prompt settlement.
Handling Overdue Invoices and Bad Debts
- Follow-Up Procedures: Implement a structured follow-up process for overdue invoices.
- Collection Agencies: Engage collection agencies for persistent non-payers.
- Write-Off Policies: Establish clear policies for writing off bad debts when necessary.
Using Technology to Improve Accounts Receivable Processes
- Automated Tracking: Use software to monitor outstanding invoices and payment statuses.
- Analytics Tools: Analyze receivables data to identify trends and improve collection strategies.
Stage 7: Payment Processing
Different Payment Methods and Their Implications
- Credit Cards: Fast and convenient but incur processing fees.
- Bank Transfers: Secure but may take longer to process.
- Digital Wallets: Increasingly popular for online transactions.
- Checks: Traditional but slower and prone to errors.
Ensuring Secure and Efficient Payment Processing
- Encryption: Use encryption to protect payment information.
- PCI Compliance: Ensure compliance with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS).
- Fraud Detection: Implement fraud detection tools to identify and prevent unauthorized transactions.
Dealing with Payment Disputes and Chargebacks
- Dispute Resolution: Have clear procedures for handling payment disputes.
- Chargeback Management: Track and respond to chargebacks promptly to minimize losses.
Integration of Payment Gateways with Accounting Systems
- Seamless Integration: Connect payment gateways with accounting software for real-time updates.
- Automated Reconciliation: Use automated systems to reconcile payments with invoices accurately.
Learn more about the frequently asked questions on O2C outsourcing by clicking here.
Stage 8: Reporting and Data Analysis
Importance of Reporting and Data Analysis in the O2C Process
Reporting and data analysis provide insights into the performance of the O2C process, helping identify areas for improvement and making informed decisions.
Key Metrics and KPIs to Monitor
- Days Sales Outstanding (DSO): Measures the average number of days it takes to collect payment.
- Order Cycle Time: Tracks the time from order placement to delivery.
- Invoice Accuracy: Monitors the rate of invoice errors.
- Payment Collection Rate: Measures the efficiency of payment collection efforts.
Using Data Analytics to Identify Process Improvements
- Trend Analysis: Identify patterns and trends to optimize processes.
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigate the underlying causes of issues to implement effective solutions.
Leveraging Technology for Real-Time Reporting and Insights
- Dashboard Tools: Use real-time dashboards to monitor key metrics.
- Predictive Analytics: Employ predictive analytics to forecast trends and prepare for future challenges.
- Reporting Software: Implement software that provides comprehensive and customizable reports.
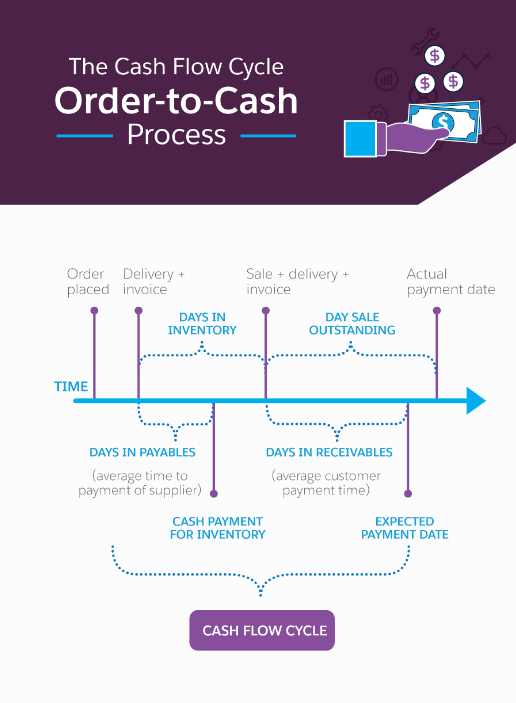
The Cash Flow Cycle in Order-to-Cash Process; Source: Salesforce
Conclusion
We have explored the eight critical stages of the Order-to-Cash outsourcing process, each vital in sculpting the efficiency and effectiveness of your business operations. By streamlining these stages, companies can not only accelerate their cash flow but also enhance customer satisfaction and operational transparency. Optimizing the O2C cycle doesn’t just translate into better business outcomes—it’s a strategic imperative in today’s competitive marketplace.
As we conclude, remember that the journey to a streamlined O2C process is continuous and demands consistent adherence to best practices. Whether it’s reducing errors in order entry, speeding up invoice approvals, or ensuring timely payment collections, each step you refine contributes to a more robust bottom line.
If you’re ready to take your O2C process to the next level, don’t hesitate to reach out. At QX Global Group, we specialize in transforming O2C cycles into seamless, efficient operations that drive business success. Contact us today to learn how our tailored solutions can benefit your organization. Together, let’s unlock the full potential of your processes and propel your business forward.
FAQs
What are the benefits of a streamlined O2C?
A streamlined Order-to-Cash (O2C) process offers numerous advantages, enhancing both operational efficiency and financial performance:
- Improved Cash Flow: By speeding up the invoicing and payment collection process, businesses can maintain a healthier cash flow, ensuring they have the liquidity to meet their obligations and invest in growth opportunities.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Efficient O2C processes reduce errors and delays, leading to quicker order fulfillment and more accurate billing, which improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automation and optimization of the O2C cycle can significantly lower administrative and labor costs, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing errors.
- Better Data Accuracy: Streamlined processes ensure data consistency and accuracy, which is crucial for making informed business decisions and maintaining compliance with regulations.
- Increased Scalability: A well-optimized O2C process can easily scale business growth, handling higher volumes of transactions without a proportional increase in resources.
- Enhanced Reporting and Insights: Improved O2C processes provide better visibility into sales and revenue data, allowing for more precise forecasting and strategic planning.
Why is the O2C cycle important?
The Order-to-Cash cycle is a critical component of a business’s operations for several reasons:
- Revenue Generation: O2C encompasses all the steps from receiving customer orders to collecting payment, directly impacting a company’s revenue stream. Efficient management of this cycle ensures timely revenue realization.
- Customer Relationship Management: The O2C cycle is integral to customer satisfaction. Timely and accurate order processing, delivery, and invoicing build trust and enhance customer relationships.
- Working Capital Management: Efficient O2C processes ensure that receivables are collected promptly, optimizing working capital and enabling the business to invest in other areas.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining the O2C cycle reduces bottlenecks and redundancies, improving overall operational efficiency and allowing businesses to allocate resources more effectively.
- Risk Mitigation: Proper management of the O2C cycle helps identify and mitigate risks related to credit, fraud, and compliance, safeguarding the company’s financial health.
What are the risks involved in the O2C process?
The Order-to-Cash process carries several risks that can affect a business’s financial and operational health if not properly managed:
- Credit Risk: Extending credit to customers involves the risk that they may default on payments, impacting cash flow and profitability.
- Operational Risk: Inefficiencies or errors in order processing, invoicing, or payment collection can lead to delays, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction.
- Fraud Risk: The O2C process can be susceptible to fraud, both internally (e.g., employee fraud) and externally (e.g., customer or third-party fraud), leading to financial losses.
- Compliance Risk: Non-compliance with regulatory requirements related to billing, taxation, and data protection can result in legal penalties and damage to reputation.
- Market Risk: Changes in market conditions, such as economic downturns or shifts in customer demand, can impact order volumes and the ability to collect payments.
- Technological Risk: Dependence on technology for automating the O2C process introduces risks related to system failures, cyberattacks, and data breaches.
- Customer Dissatisfaction: Errors and delays in the O2C process can lead to poor customer experiences, potentially resulting in lost business and negative word-of-mouth.
Originally published May 23, 2024 01:05:29, updated Nov 25 2024
Topics: Finance and Accounting Outsourcing Services, Order-to-cash cycle







